Two aspects arise in the robot applications in industrial production line. One related to the design of robot work cell which may consist of more than one robot and more than one machine. The other is related to control system that will coordinate the activities among various components of work cell.
ROBOT WORK CELL LAYOUTS:
Robot work cells can be organised in to various configurations depending on the requirement of the manufacturing line. However three are in common:
- Robot-Centered work cell
- In-line robot work cell
- Mobile robot work cell
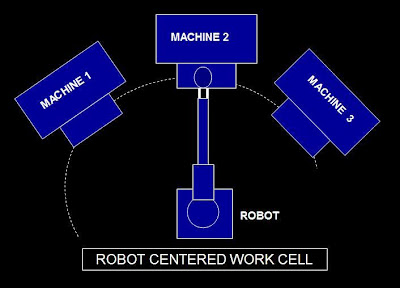
Here robot is located approximately at the center of the cell and the equipments are arranged within the reach of robot.
The robot services the equipments in a particular sequences of its operation.
The service operations are loading the equipment with a partially finished product and unloading it from the equipment. Some time Robot should wait (or idling) till the processing by a machine is completed. ( eg: CNC machining). Some time machine is to wait till it gets the robot service. (eg: Stamping)
In some applications, robot can perform production (processing) operations. Applications in this case are welding, polishing and painting.
Parts are to be supplied to robot to perform a pick and place (loading/unloading) or a processing operation. Conveyors, part feeders, delivery chutes and pallets are the means of accomplishing the supply of parts to robot.
Discrete part productions such as die-casting, machining, plastic molding and other similar production operations can be accomplished by this work cell.
IN-LINE ROBOT WORK CELL:

Refer Figure : The robot is located along a moving conveyor and to perform tasks on the product that is coming on the conveyor. Many in-line robot work cells involve more than one robot. One common example is : Car Body assembly; robots are positioned along the assembly line to spot-weld the car body frames and panels.
There are three categories of transfer system that can be used with in-line robot cell configuration:
- Intermittent Transfer
- Continuous transfer
- Non-synchronous transfer.
No comments:
Post a Comment